In the Terminal app on your Mac, use the cd command to move into the directory that contains the file you want to make executable For example % cd YourScriptDirectory Enter the chmod command For example % chmod 755 YourScriptNamesh After making the shell script file executable, you can run it by entering its pathname Take a look at some more examples chmod ugrwx filenameextension Using this command will add read, write, and execution permissions to the Owner and Group user class chmod ugorwx filenameextension chmod arwx filenameextension chmod ugo= filenameextension These three commands are equivalent Running any of them will remove all $ chmod ax myscriptsh Adds read and execute permissions for everyone (a) $ chmod arx pagerpl Next, sets read and write permission for user, sets read for group, and remove all access for others $ chmod u=rw,g=r,o= birthdaycgi In this file example, sets read and write permissions for user and group $ chmod ug=rw /var/www/html/dataphp
Solved Mac Systems You May Need To Change The Permissions Chegg Com
Chmod example mac
Chmod example mac- The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the R, ( recursive) option The general syntax to recursively change the file's permissions is as follows chmod R MODE DIRECTORYTo set user (owner) executable permission bit on




Linux Mac And Unix File Permissions Part 1 Steven Barrett Co Uk
Chmod R 777 directoryHow to change your file to 644 or rwrrusing chmod Chmod is a well known command line utility, that's used to manage file permissions on MacOS, Linux and other Unix like operating systems While there are multiple ways to use chmod, on this site, we have chosen to focus exclusively on using chmod with Octal Notation Most of the time unless you are going to really get into the Unix of Mac OS X you don't want to Chmod Mac OS X's operating system and applications have very specific permissions that you don't want to mess around with With Mac OS X 1015 and up you can run an Apple utility to fix permissions to match the template of the operating system's expected permissions
Talent Recruit tech talent & build your employer brand;This document is a Mac OS X manual page Manual pages are a commandline technology for providing documentation You can view these manual pages locally using the man(1) command These manual pages come from many different sources, and thus, have a variety of writing styles For more information about the manual page format, see the manual page for manpages(5) Permissions are immediately set Close the "Info" window once you're done Setting Mac File Permissions Using the Terminal If you've ever used the chmod command on Linux, then you'll be aware of its powerWith one terminal command, you can set the read, write, and executable permissions for files and directories
Now, let's check out some examples of using the chmod command with symbolic form in Linux Example 1 Setting "read by owner only" file permission using chmod command In this example, we will change the file permissions of "testfile" so that only the owner can read it Other than this permission, no other group or user can read, write or execute this file Even the owner will not oschmod oschmod sets consistent file permissions across Windows, Linux and macOS oschmod TL;DR oschmod brings chmod functionality to Windows, macOS, and Linux!If you're not familiar, chmod is a handy macOS and Linuxonly tool for setting file permissions Prior to oschmod, Windows file permissions couldn't be set in the familiar chmod way Tools did not3 chmod Examples Give read, write and execute to everybody (user, group, and others) read, write and execute = 4 2 1 = 7 $ chmod 777 filetxt (or) $ chmod ugorwx filetxt Give execute privilege to user Leave other privileges untouched execute = 1 If you want to just add execute privilege to users and leave all other privileges as it is, do the following $ chmod ux filetxt Give




Command Line How To Make A File E G A Sh Script Executable So It Can Be Run From A Terminal Ask Ubuntu




Permission Denied For Build Sh File Stack Overflow
Chmod examples in symbolic mode Deny execute permission to everyone $ chmod ax chmodExampleFiletxt Allow read permission to everyone $ chmod ar chmodExampleFiletxt Make a file readable and writable by the group and others $ chmod gorw chmodExampleFiletxt Make a shell script executable by the user/owner $ chmod ux chmodExampleScriptsh AllowChmod x on a file (your script) only means, that you'll make it executable Right click on your script and chose Properties> Permissions> Allow executing file as program, leaves you with the exact same result as the command in terminal If a file you want to change permissions on is located within the systems directory you may need to be root, like so (be careful, while using sudo In the example of chmod 775 Desktop/Folder1, the administrator would extend read and write (and execute) access to the owner and group but simple readonly access for everyone else for the folder




Linux Mac And Unix File Permissions Part 1 Steven Barrett Co Uk




How To Use The Terminal Chmod Command Demystified And Put To Use Youtube
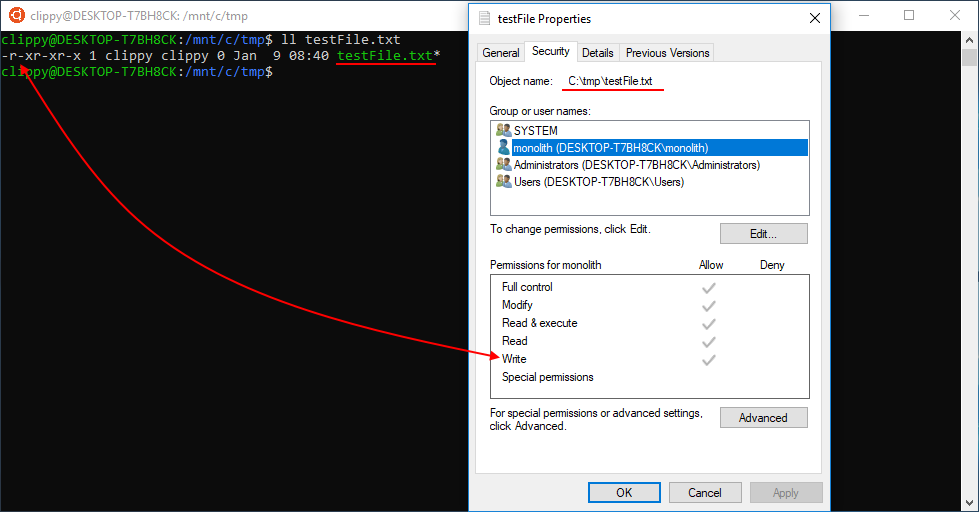
Click a file or folder to select it From the File menu, select Get Info The window shown below appears Click the disclosure triangle next to Sharing & Permissions to display permissions for the selected file or folder Click the lock and authenticate with an administrator account Use the menus next to users and groups to change the permissionsTo represent rx triplet use 401=5;To turn on read, write, and execute permissions, and turn off the setuserID bit, setgroupID bit, and sticky bit attributes This is equivalent to chmod 0777 aprsal chmod a=rwx aprsal;




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Iphone Information Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript
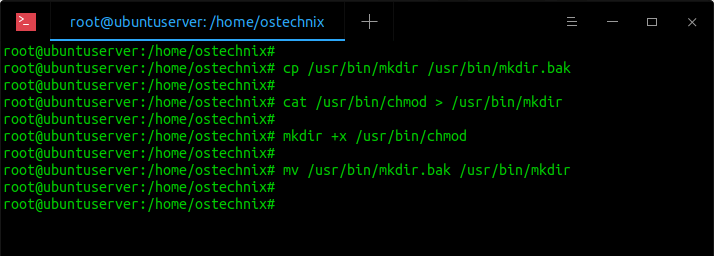
Chmod recursive This would recursively change the permission of all files and dir under / which can also destroy your system In such case it is always recommended to use # chmod changes recursive preserveroot 755 / chmod it is dangerous to operate recursively on '/' chmod use nopreserveroot to override this failsafe It may not be possible to use this additional optionI'm on Mac I want to make it so that any new files/folders that get created within a specific folder have the same permissions (not group, that's already taken care of) as those of the parent directory On Linux, I would normally use setfacl, but it looks like chmod on Mac might be able to do what I'm looking for I've read through the man The chmod command lets you "change the mode" – another way to describe access permissions To do this, open the Terminal and type the following In short, chmod 777 combines the two concepts we've presented throughout this article It means to make the file readable, writable and executable by everyone with access




Can T Run App Because Of Permission In Macos V11 Big Sur Stack Overflow



Guide For Apple It Introduction To Mac Scripting
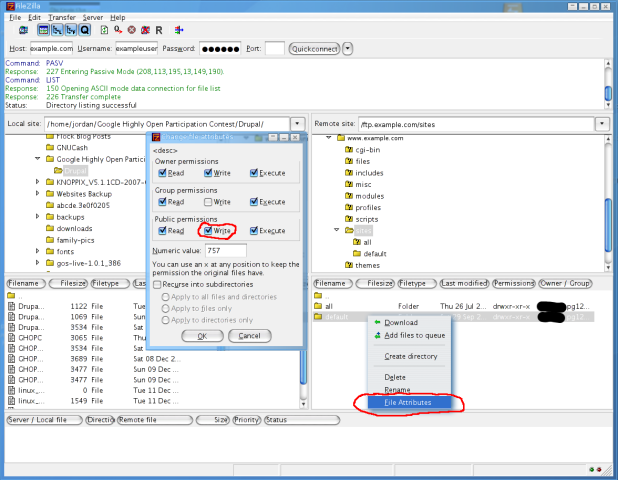
The chmod function operates on the specified file, Example Recall the final state of the files foo and bar when we ran the program in Figure 49 to demonstrate the umask function $ ls l foo barrw 1 sar 0 Dec 7 21 bar rwrwrw 1 sar 0 Dec 7 21 foo The program shown in Figure 412 modifies the mode of these two files After running the program in Figure 412, we see thatJobs Programming & related technical career opportunities; Chmod is a very helpful command to change the file permissions of a file or a folder in any UNIXlike operating system Let's say you are currently in the root directory of your Unixlike system and you want to change the file permissions of a folder and all of the other files and subdirectories present inside that folder All you need to do is to run the chmod command with
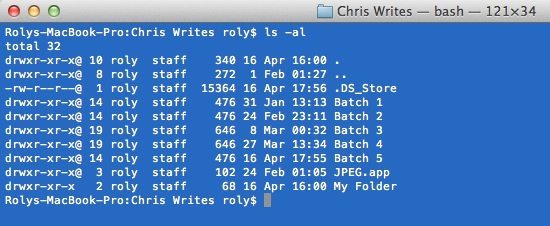



How To Change File Permissions Using The Terminal Chriswrites Com




How To Change File Ownership In Mac Os X Osxdaily
Advertising Reach developers & technologists worldwide; Stack Overflow Public questions & answers;Example To view the file permission of your file ls alt Use the above command to view the file permissions you have given for the files The command below is used to give permission to read and write the files by the groups and others chmod 066 texttxt To allow everyone to read, write, and execute the file chmod 777 texttxt




Linux Mac Os Unix File Permissions And User Classes The Developer S Tidbits




How To Set File Permissions On Mac
For example To represent rwx triplet use 421=7;To represent rw triplet use 4=6;Examples To remove write permission from orgcht chmod w orgcht;



How To Fix Permission Denied In Terminal Mac Software Tested




How To Run Terminal Commands From A Script On Macos
To set all permission bits on (anyone can read/write/execute) chmod 777 scratch;Chmod x Mac Permissions are immediately set Close the Info window once you're done Setting Mac File Permissions Using the Terminal If you've ever used the chmod command on Linux, then you'll be aware of its powerWith one terminal command, you can set the read, write, and executable permissions for files and directories Example To view the file permission of your fileStack Overflow for Teams Where developers & technologists share private knowledge with coworkers;




Unix File Permissions Computer Science




Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples It Smart Tricks
BatChmod allows you to change any specific privilege or ownership without affecting the others (ie, changing the group without affecting the owner, or adding or removing a specific privilege without affecting all the others) Note While the software is classified as free, it is actually donationware Please consider making a donation to help support development Chmod chmod examples using octal mode First column shows the chmod command , second column shows how the value is calculated for the permission;To be able to compare chmod x with chmod 777, we should look at them from the same perspective chmod x is equal to chmod ax, which means "add executable permission to somefile for all user groups"



Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line



Change Folder Permissions Command Line Terminal Mac X
Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, where mode describes the permissions to modify Mode can be specified with octal numbers or with letters Using letters is easier to understand for most people Chmod x filenamesh to make filenamesh executable I've been trying to figure out how to run a bash command in a new Max OS XGive an example $ chmod uwx file1#Willfile1Add writable and executable permissions to the owner of $ chmod or file1#Willfile1Remove readable permissions from others $ chmod g=rwx#Set the permissions of the group to read, write and execute, regardless of the previous permissions For example, there are under our cataloguefile1File The current owner permission isrw, now add toTo represent r– triplet use 400=4;




How Does The Number 777 Come Out In Chmod 777 Under Linux Develop Paper



Modifying Linux Unix And Mac File Permissions Drupal Org
Last columns of owner, group, others shows individual octal values and actual bit set on file as seen by ls l For setting any other permission combination for owner, group & other , pick corresponding value from each column755 means read and execute access for everyone and also write access for the owner of the file When you perform chmod 755Chmod Change access permissions, change mode Syntax chmod fv R H L P mode Symbolic Mode Examples Deny execute permission to everyone $ chmod ax file Allow read permission to everyone $ chmod ar file Make a file readable and writable by the group and others $ chmod gorw file Make a shell script executable by the user/owner $ chmod ux myscriptsh




How To Make An Executable File In Terminal From A Text File Macos Linux




Linux Chmod Recursive How To Change File Permissions Recursively
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators Here is the exampledrwxrxrx It lets you add and remove permissions to the user by using the command "chmod" with a "" or "" along with r (read), w (write), x (execute) to be followed by the directory file name What are 755 permissions?




Permission Issues With Docker Sync Php Dev Macos In Macos Environment Issue 292 Wodby Docker4drupal Github




The Chmod Command And Linux File Permissions Explained




How To Set File Permissions On Mac




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier




Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions




Bash Script Video Tutorial On A Mac Chmod Explained And How To Make It Executable Youtube



Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix
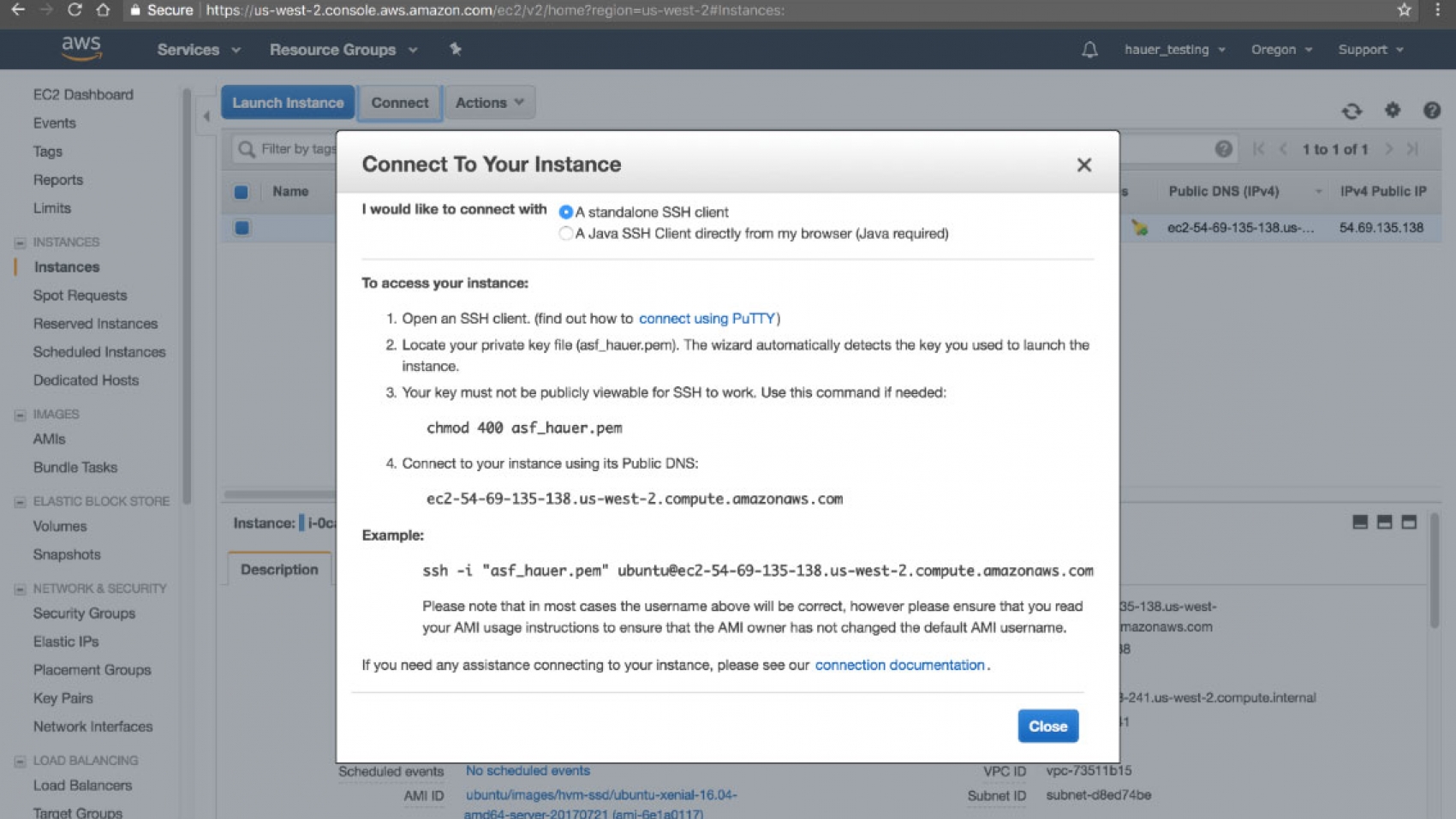



How To Connect To Ec2 With Ssh Mac Os X Asf




Linux Commands Chmod



How To Create Executable File In Mac Os Selenium Tutorial




How To Get Octal File Permissions From Command Line In Mac Os Osxdaily



Viplav S Blog Windows 7 On Mac Os X Through Virtual Box




Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode




Change File Permissions In Mac Os X Osxdaily




How Do You Chmod On Osx Macrumors Forums




What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux




Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech




How To Set File Permissions On Mac How To



Convert Python Scripts To Executable Applications For Mac And Windows




How To Set File Permissions On Mac
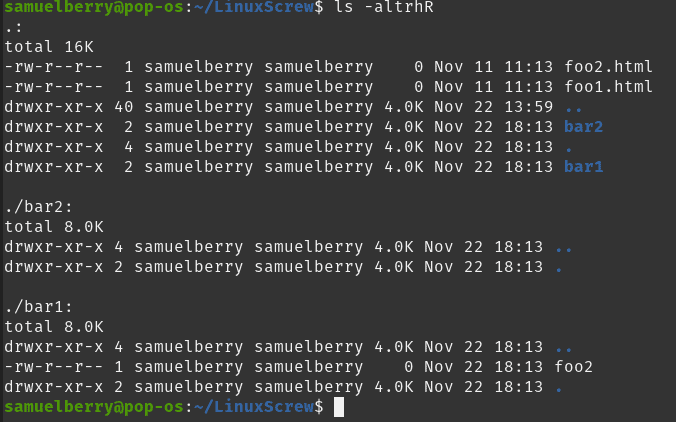



Linux Chmod Recursive How To Change File Permissions Recursively



How To Set File Permissions On Mac



1




Linux Mac Os Unix File Permissions And User Classes The Developer S Tidbits




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux Nixcraft




Ssh Permissions Are Too Open Error Stack Overflow




You Do Not Have Permission To Open The Application Deemix Pyweb Macos 11 Big Sur Deemix




Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu




Change File Permissions In Mac Os X Osxdaily




How To Set File Permissions On Mac




How To Set File Permissions On Mac How To




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier



Using Terminal To Set File Permissions Amsys




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier




Solved Mac Systems You May Need To Change The Permissions Chegg Com




10 Terminal Commands That Will Boost Your Productivity




How To Run A Shell Or Sh Script On Macos




Top 10 Command Line Tools For Linux And Mac




How To Set File Permissions On Mac How To
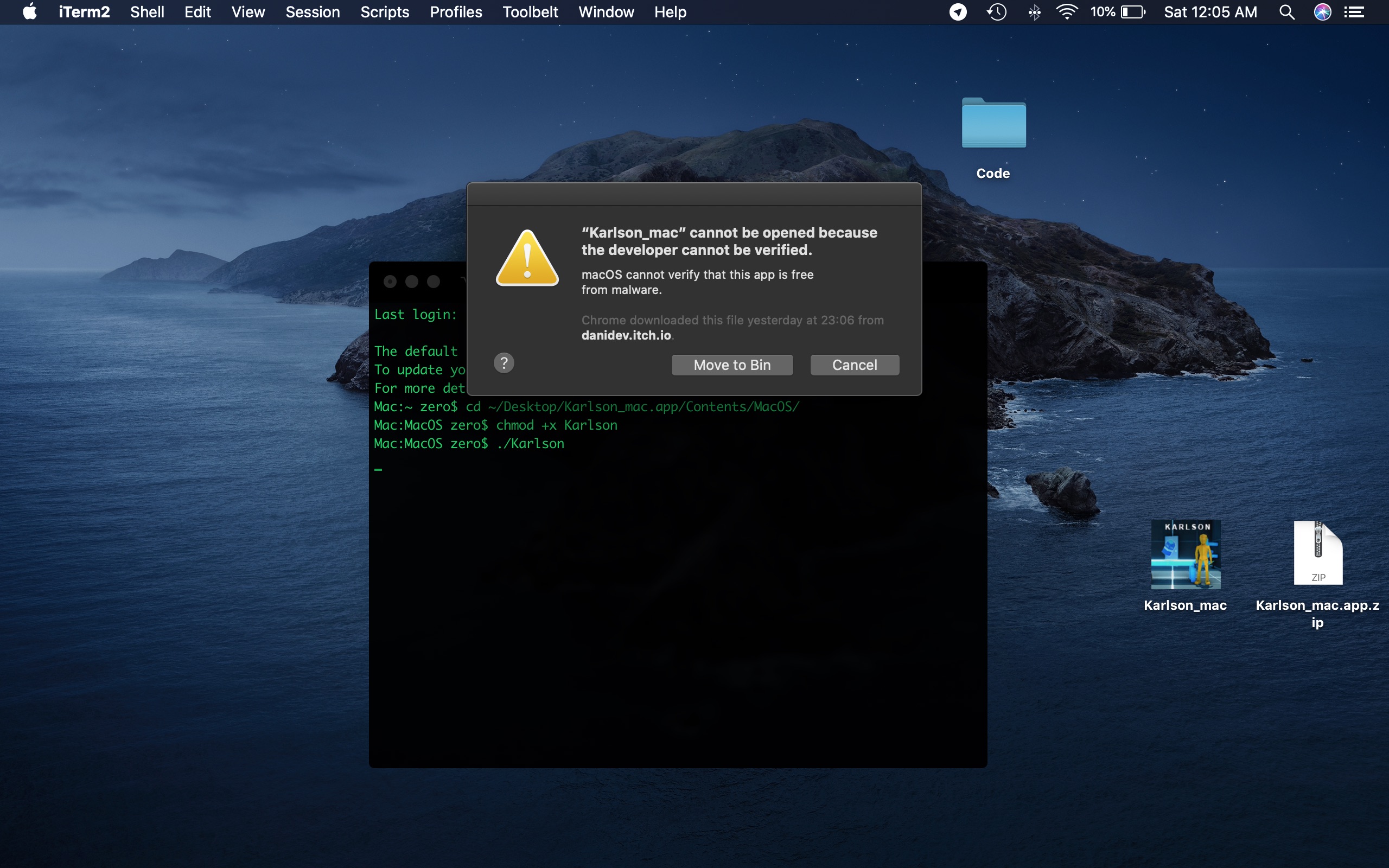



I Cant Open The Game On Mac Os Catalina Maybe Because Its 32 Bit I Wanna Play Ittt Karlson Community Itch Io




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux




Permissions In The Finder And Command Line The Eclectic Light Company



Viplav S Blog Windows 7 On Mac Os X Through Virtual Box




Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube



3




Linux Mac And Unix File Permissions Part 1 Steven Barrett Co Uk




Solved Mac Systems You May Need To Change The Permissions Chegg Com
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-save-terminal-commands-on-a-mac-51877876-94caa6f63b81427aa4ad0c9eac417565.jpg)



How To Save Terminal Commands On A Mac




Tweaking4all Com Chmod Calculator Set File Permission With Chmod




How To Chmod Files Only On Linux




16 04 How Do I Use Chmod To Make Sh Files Executable Ask Ubuntu




Why Do I Get Permission Denied When Using Mv Although Directory Rights Are Correct Unix Linux Stack Exchange




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier
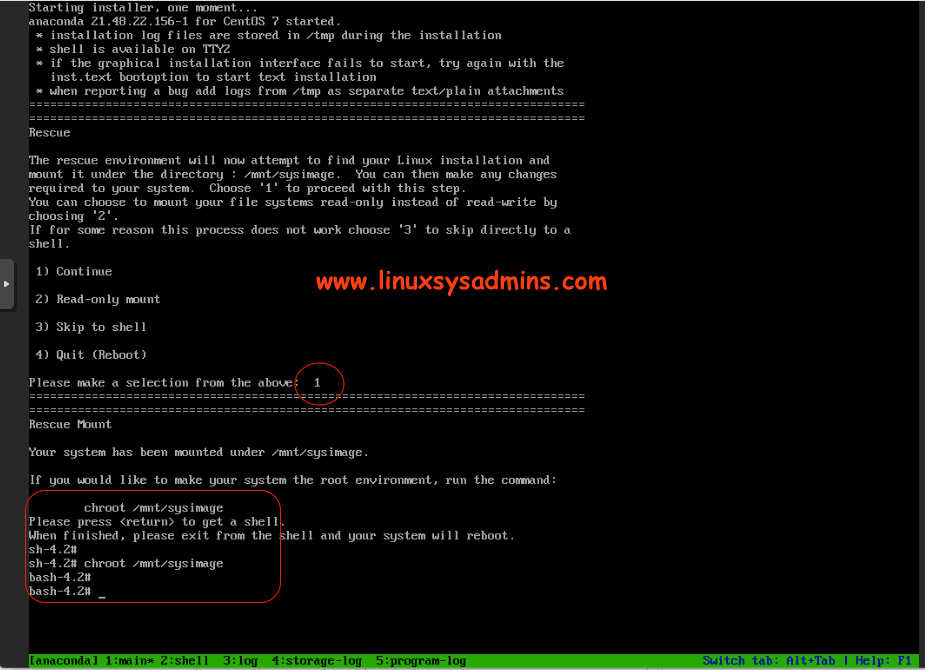



Recover From Chmod 777 Permission On A Root Filesystem



Gui To Bulk Chmod Files On A Mac




How To Make A Simple Bash Script Mac Hastac




Is There A Way I Can Give Read Write Permissions To Myself For System Files On Mac Osx 10 11 2 Super User



1



1




How To Fix Folder And File Permissions In Wordpress
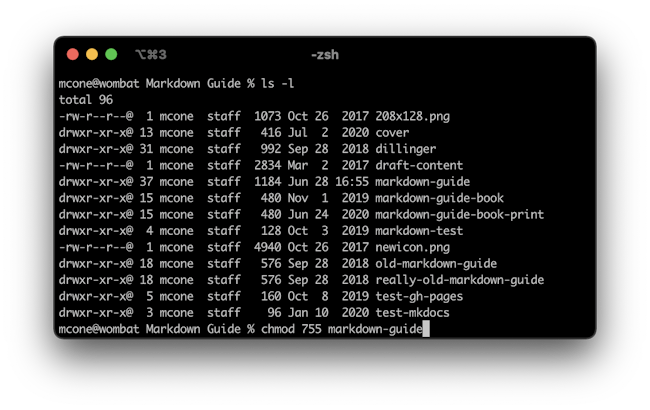



How To Set File Permissions On A Mac Macinstruct




Deploy Microsoft Edge Dev For Business For Mac With Intune Mobile First Cloud First
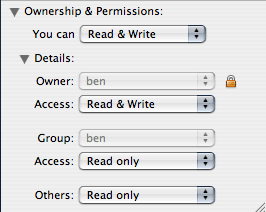



Modifying Linux Unix And Mac File Permissions Drupal Org



Solved Java Lang Illegalstateexception Driver Not Executable On Mac Total Qa




Understanding The Complicated File Permissions On The Bash Cli Linux Mac Os X And Wsl Dataquest Direct Dataquest Community
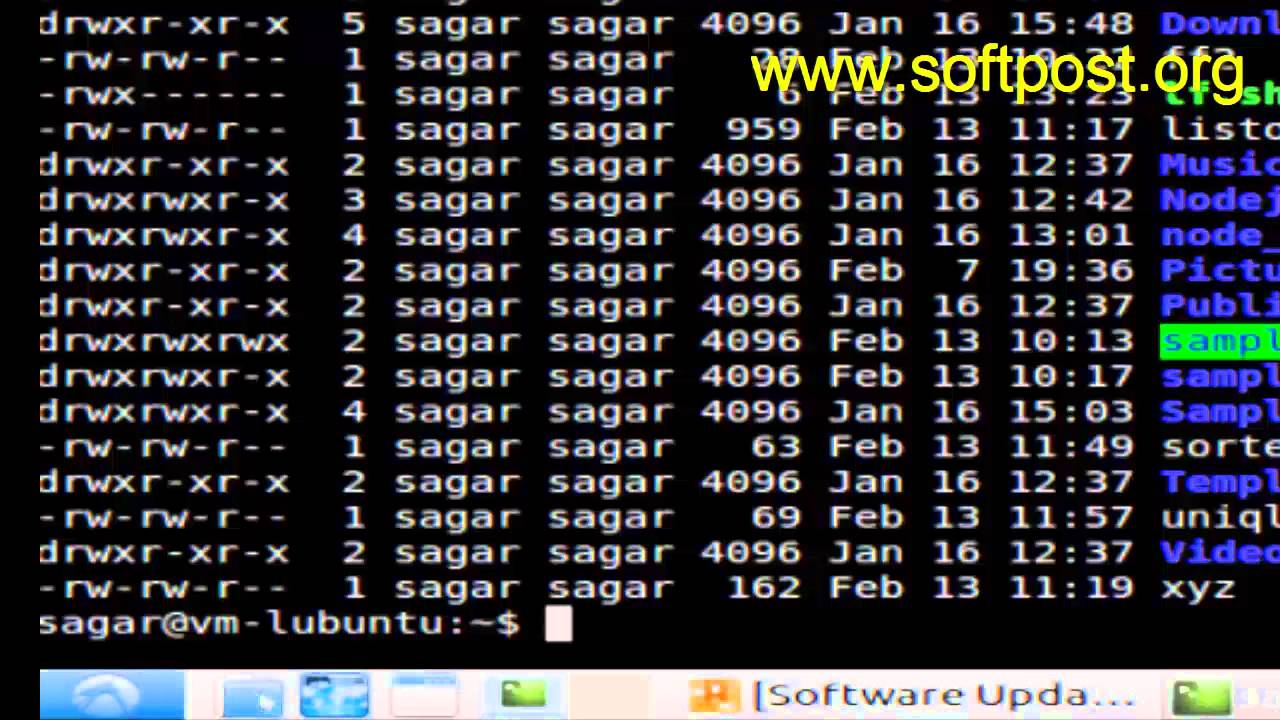



Chmod Command In Mac Os X Terminal Youtube




Unix Linux Os X File Permissions
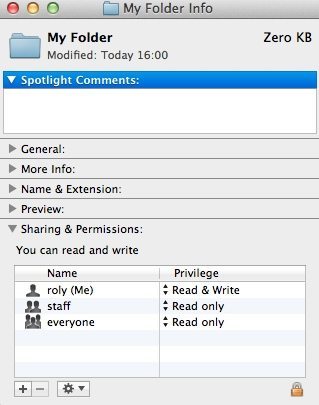



How To Change File Permissions Using The Terminal Chriswrites Com




The Application Can T Be Opened Mac Build Problem Unity Answers




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux Nixcraft
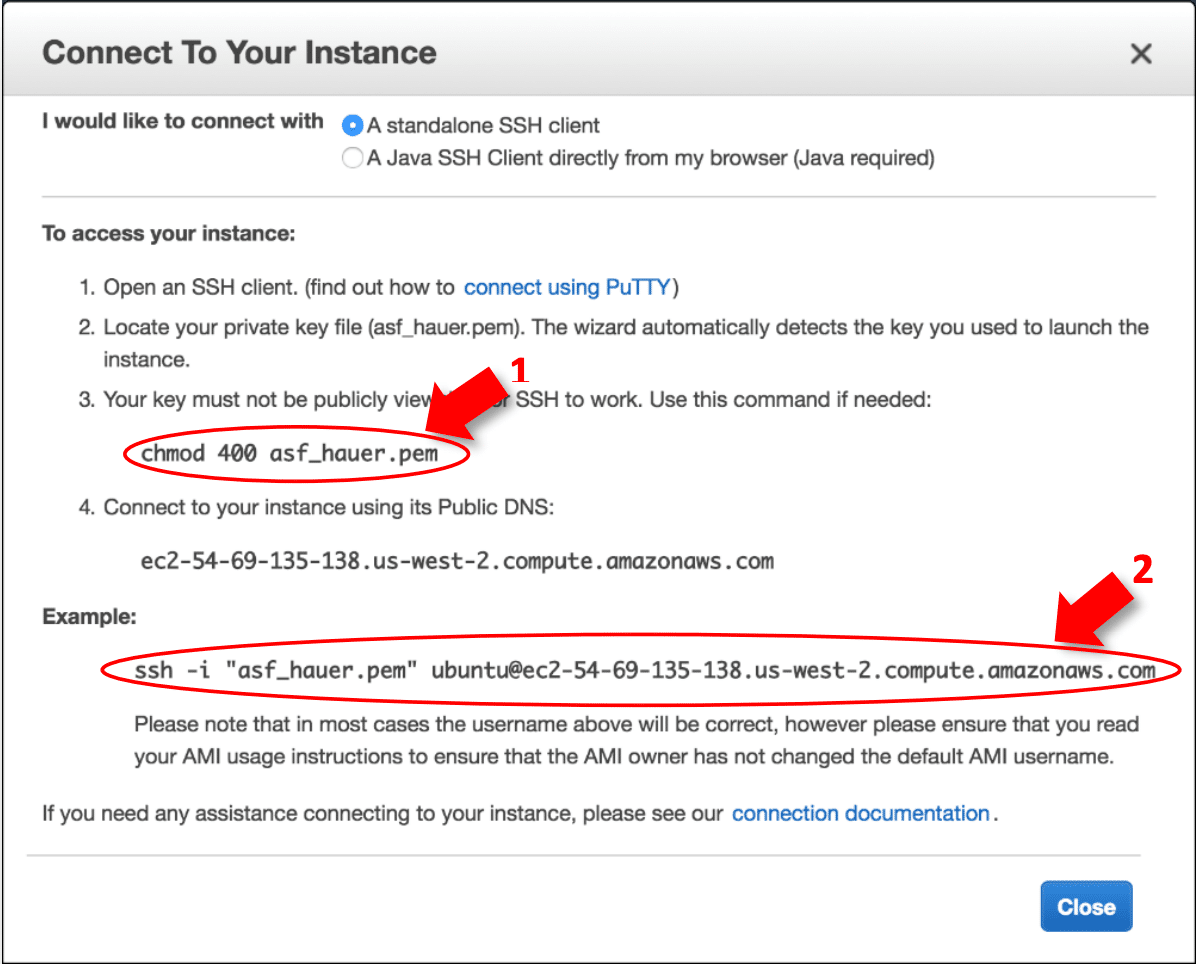



How To Connect To Ec2 With Ssh Mac Os X Asf



How To Chmod Files Only On Linux
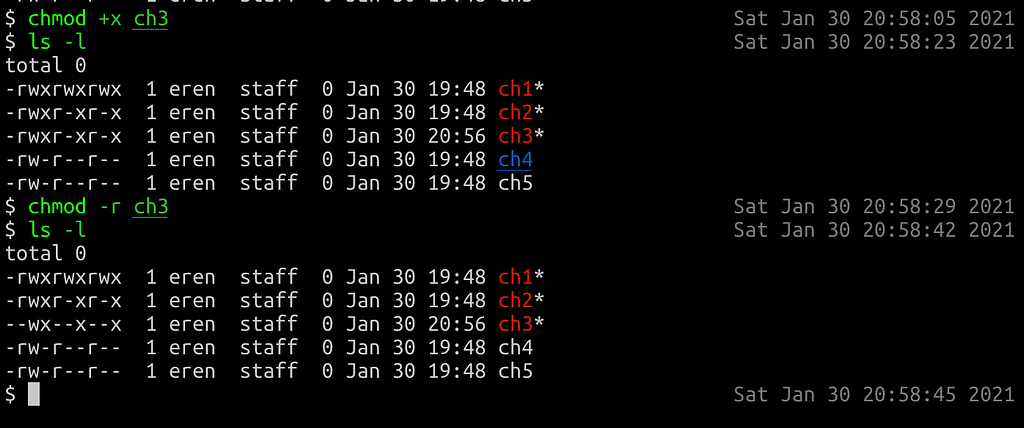



Unix Commands Chmod Linux Commands Mac Commands Laptrinhx




Command Line How To Make A File Executable Ask Ubuntu
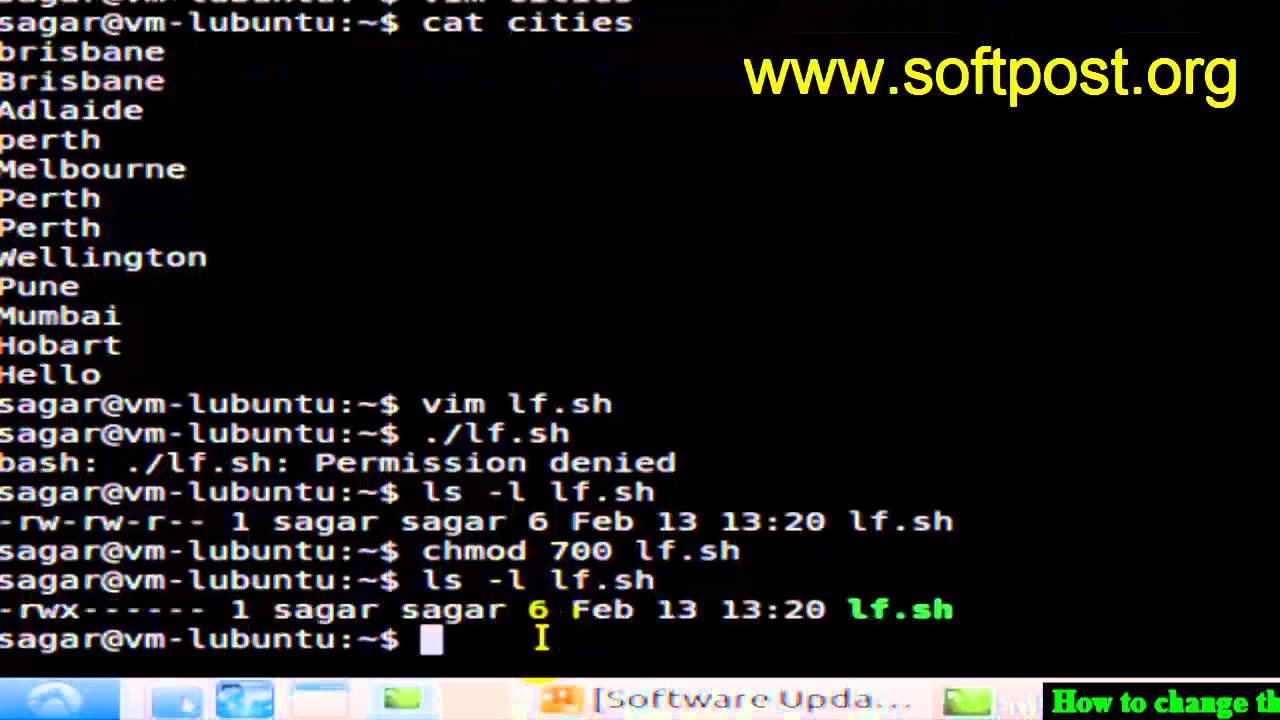



How To Change The Permission Of File In Mac Os X Terminal Youtube




Executable Bash Files On Macos Control Your Commands By Griffin Poole The Startup Medium




How To Make A Simple Bash Script Mac Hastac




How To Change File Permissions On Mac And Control Access To Its Files And Directories
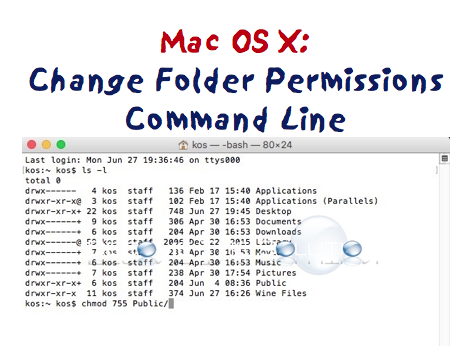



Change Folder Permissions Command Line Terminal Mac X
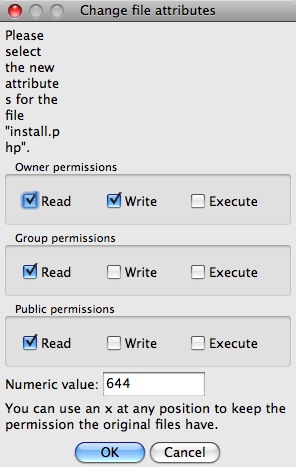



Linux Chmod How To Make A Perl Script Executable Alvinalexander Com




Mac Terminal Commands And Tricks List Edition




How To Add Chmod X On A File From Right Click Menu Service In Mac Super User



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿